There are scenario when a system is not ready & this can act as a blocker for development of UI or related backed system. Now what to do??
We can mock the system with help of mock-server https://www.mock-server.com
Benefits of using mock-server
- Polyglot
It supports following ways to setup and customize the mock-server
- JavaScript (both browser API & Node.js module)
2. Multiple way to run mock-server
- programmatically via a Java API in an @Before or @After method
- using a JUnit 4 @Rule via a @Rule annotated field in a JUnit 4 test
- using a JUnit 5 Test Extension via a @ExtendWith annotated JUnit 5 class
- As a Docker container in any Docker enabled environment
- via a Helm chart in any Kubernetes environment
- from the command line as a stand-alone process in a test environment
- via a Maven Plugin as part of a Maven build cycle
- As a Node.js (npm) module from any Node.js code
- As a Grunt plugin as part of a Grunt build cycle
- As a deployable WAR to an existing application server
3. Mockserver-UI
MockServer has a UI that can be used to view the internal state within MockServer, including:

Hands on using Mock-Server
- Run mock server (using java command line)
java -jar <path to mockserver-netty-5.11.1-jar-with-dependencies.jar> -serverPort <port>
2. Verify mock server via mock-server ui. We can
open the url http://hostname:port/mockserver/dashboard

3. Now we will setup few expectations using rest api
What is expectations :
An expectation defines the action that is taken, for example, a response could be returned
When MockServer receives a request it matches the request against active expectations that have been configured, if no matches are found it proxies the request if appropriate otherwise a 404 is returned.
3.1 Expectation :
Expectation to match a given path and method GET and return configured response
Curl to setup expectation
curl — location — request PUT ‘http://localhost:1080/mockserver/expectation' \
— header ‘Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded’ \
— data-raw ‘{
“httpRequest” : {
“method”: “GET”,
“path” : “/health”
},
“httpResponse” : {
“body” : “i am up “
}
}’
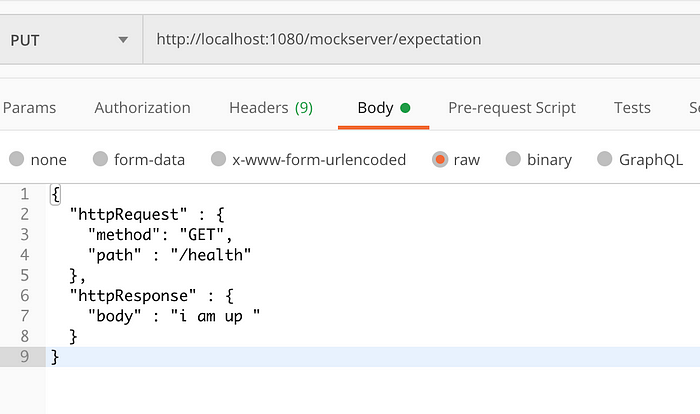
Now expectation is configured we can hit the url to get the response
curl — location — request GET ‘http://localhost:1080/health'

3.2 Expectation match header using regex.
We can create expectation to match a request header with regex.
Curl to setup the same.
curl — location — request PUT ‘http://localhost:1080/mockserver/expectation' \
— header ‘Content-Type: text/plain’ \
— data-raw ‘{
“httpRequest”: {
“path”: “/some/path/regexheadermatch”,
“headers”: {
“Custom.*”: [ “” ]
}
},
“httpResponse”: {
“body”: “request matching header via regex”
}
}’
Now we can hit the url to see the response

On similar lines we can configure the mock-server using rest api
Meta Command on Mock-Server
- Getting java code for all active expectations
We can get java code for all expectation using rest api call
curl — location — request PUT ‘http://localhost:1080/mockserver/retrieve?type=ACTIVE_EXPECTATIONS&format=java'

Referrence
